Stats-MaxChildren.sql 2016-02-12
 |
| Result from Stats-MaxChildren.sql in SQLiteSpy |
Exploit your RootsMagic family tree database with SQLite Tools
Stats-MaxChildren.sql 2016-02-12
 |
| Result from Stats-MaxChildren.sql in SQLiteSpy |
This page is in response to a question posed in the RootsMagic Forums by member DeliChef in the topic Bulk File Name Change For Hundreds of Family Letters?. He had named the files using the format MM_DD_YYYYPersonName, i.e., the date of the letter followed by name of the sender. To improve the utility of Windows File Explorer, he wanted to change the format to YYYY_MM_DDPersonName so they would sort by name chronologically. They were already linked to the RootsMagic Media Gallery and renaming the files would break the links. The Fix Broken Media Links tool is of no help in this case and manually changing the media item for hundreds of files was too daunting. So he sought help. This page describes a solution that could be adapted to other systematic name revisions.
This solution uses SQLite to query the MultiMediaTable for file names beginning with the MM-DD-YYYY format and generates a set of Windows command line statements that copy these files to a new location with their rearranged names. It also produces a set of SQLite statements that update the MultiMediaTable with the new path and filenames.
N.B., the script was written with “-” instead of “_” as the separator between the date elements and should be edited accordingly to suit your particular needs. Any systematic name pattern can be changed to another pattern.
Here’s an example of the commands produced to relocate and rename the files, copied from the vCmd View created in the database by the script
:
XCOPY "C:SDGoogle Drivegenealogymedia7-25-1900Shaw(Wright)Letitia-PlayCopy.jpg" "C:SDGoogle DrivegenealogymediaNewFolder1900-07-25Shaw(Wright)Letitia-PlayCopy.jpg" XCOPY "C:SDGoogle Drivegenealogymedia12-01-1949Secombe, Harry (sure).jpg" "C:SDGoogle DrivegenealogymediaNewFolder1949-12-01Secombe, Harry (sure).jpg" ...
and the corresponding SQLite statements to relink the renamed files are copied from the vSQL View created in the database by the script:
BEGIN; UPDATE MultiMediaTable SET MediaPath = 'C:SDGoogle DrivegenealogymediaNewFolder', MediaFile = '1900-07-25Shaw(Wright)Letitia-PlayCopy.jpg' WHERE MediaID = 18; UPDATE MultiMediaTable SET MediaPath = 'C:SDGoogle DrivegenealogymediaNewFolder', MediaFile = '1949-12-01Secombe, Harry (sure).jpg' WHERE MediaID = 19; ... COMMIT;
The XCOPY commands are copied into a DOS batch (.bat) or Windows command line script (.cmd). It is advisable to create the desired destination folder before running this file from the Command Language Interpreter because it may ask whether the target is a folder or a file if the folder does not exist. The correct answer is “file” for which it will create the missing folder(s) in the path.
The SQLite statements are copied into the SQL editor of a SQLite manager such as SQLiteSpy and executed on the database.
The script creates 4 temporary SQLite Views in the RootsMagic database:
This takes longer to describe than to execute. The slowest part of the process will be the copying of the files. Alternatively, the script could be revised to RENAME files (faster but a little more daring…)
2021-11-22 Compatible with #RM8
See Maps – markers proportional to number of events for an extension of this script to produce results suitable for mapping.
This script produces a list that I think is useful for finding the places that lack an abbreviated name or geographical coordinates and for tackling first the ones having the biggest payoff. For example, a place that is only used once in total or only once for a person does not need a shortened name. On the other hand, a place that is greatly used will add much to a report such as the Place List option “Print events near a place” once it is geo-coded and narratives will sound less repetitive using the abbreviated name. So the list provides two counts:
The list includes:
-- Place_Frequency.sql /* 2013-03-25 Tom Holden ve3meo rev 2013-03-25 TotEvents error corrected rev 2013-03-27 Place:Abbrev corrected to Place:short in comments. TotEvents extended to include family events. MaxEvents remains for Indiv only. Unused places also listed. Returns frequency of use for each Place in the database - total events for each place - max number of events for any person and a person having that max number (family events not counted) Useful for finding places in need of Abbreviations or Geocoding or Unused */ SELECT Places.PlaceID ,EventsByPlace AS TotEvents -- total events for place ,Events AS MaxEvents -- Max Events for a place by Person (Indiv facts) ,PersonID -- Person having the max events for that place ,NAME AS Place -- place name used by Place or Place:original in sentence template ,Abbrev -- value used by Place:short in sentence template ,Latitude / 10000000.0 AS Latitude -- in decimal degrees, North+ ,Longitude / 10000000.0 Longitude -- in decimal degrees, East+ ,Normalized AS Standardized -- the Standardized value in the Edit Place screen FROM PlaceTable Places LEFT JOIN ( SELECT PlaceID ,PersonID ,MAX(Events) AS Events FROM ( -- table of Places for which Persons have events and the number of events for each combinatio SELECT PlaceID ,OwnerID AS PersonID ,COUNT() AS Events FROM EventTable WHERE OwnerType = 0 -- Individual, not Family, events GROUP BY PlaceID ,OwnerID -- to aggregate number of events by Place-Person combo ORDER BY Events ASC -- to order so that the next GROUP BY PlaceID will extract the highest value of Events for a Place ) GROUP BY PlaceID ) AS PersonEvents ON Places.PlaceID = PersonEvents.PlaceID LEFT JOIN ( -- table of total events per place SELECT PlaceID ,COUNT() AS EventsByPlace FROM EventTable GROUP BY PlaceID ) AS AllEvents ON Places.PlaceID = AllEvents.PlaceID WHERE PlaceType = 0 -- user defined Place; excludes Place Details and Temples --GROUP BY Places.PlaceID -- to aggregate TotEvents and extract highest value of MaxEvents for Place-Person combo ORDER BY MaxEvents DESC -- initial view puts the highest max events first as priority for attention ;
2021-11-22 Compatible with #RM8
An earlier script, Places – Frequency of Use, produced a result set that counted the number of events in each Place in a RootsMagic database. This script builds on that query to generate a comma-delimited data set suitable for uploading to GPSVisualizer.com to generate a map with circle markers that are proportional in size to the number of events.
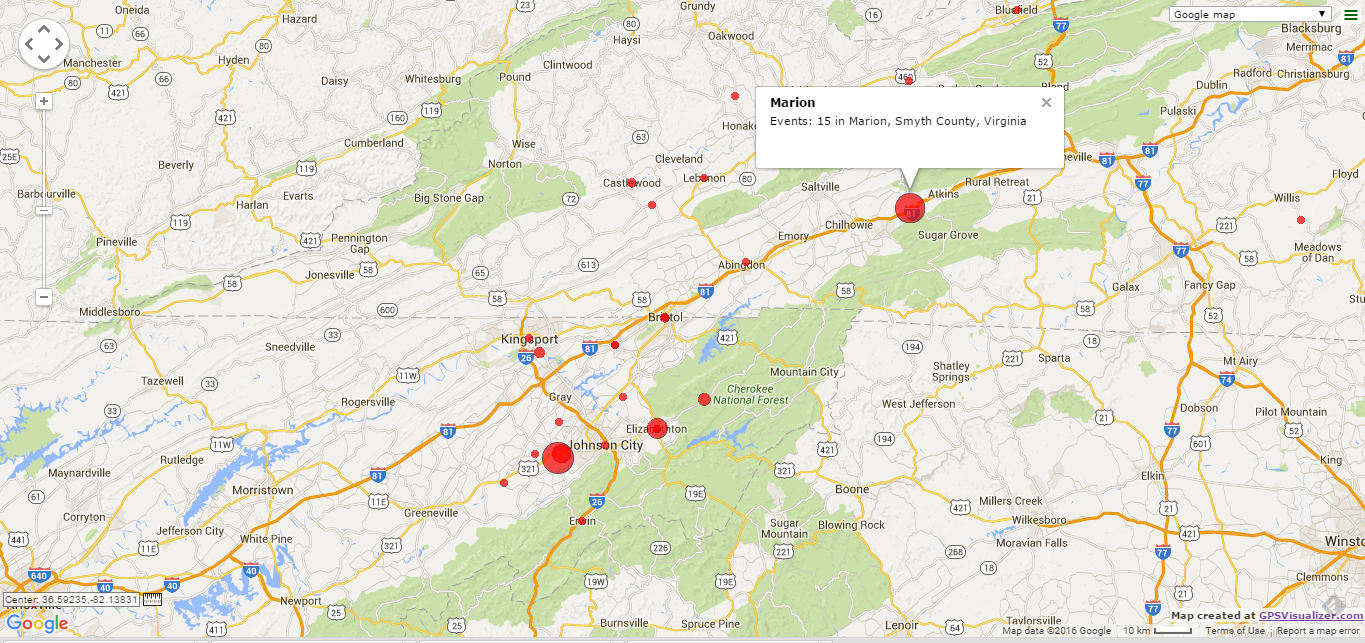 |
| Example of a proportional symbol map generated from data extracted by Place_Frequency_GPSVisualizer. |
The script produces a result set similar to the screenshot below from SQLiteSpy. 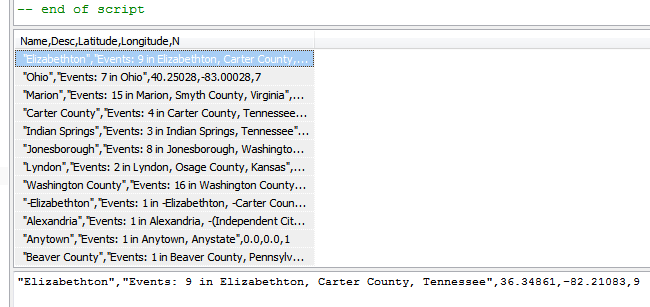
Select any row, then Ctrl-A to select all and Ctrl-C to copy all selected to the Windows Clipboard. You can choose to paste directly into the GPSVisualizer form or into a text editor (NotePad) and save it to a file with the .csv extension for upload and reuse.
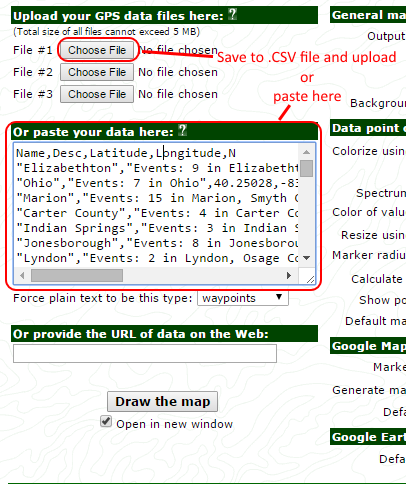
Place_Frequency_GPSVisualizer.sql
When the person highlighted in Pedigree View or Family View is linked to more than one spouse, RootsMagic 7 lets you select the one to be shown from the dropdown Spouse list. This list also offers a “Rearrange spouses” control which sets the order of the spouses in the dropdown list and the order in which spouses are displayed in the Descendant and Timeline Views, the Edit Person screen and in certain reports. The Rearrange Spouses dialog allows both manual ordering and “Sort by Marriage Date”. This control operates only on the spouses of one person at a time. A wish has been expressed for a global Sort by Marriage Date. Furthermore, an emigre from Family Tree Maker pointed out that it also factors in the birth date of the first child in the case of an unwed couple. These requests may never see the light of day within RootsMagic but here is a script that does the global job in the interim.
Some words of caution. For spouses without marriage events or children, neither the script nor the current RootsMagic function can do anything but sort them to the top of the list. And this script will override sequences arranged manually through RM’s Rearrange Spouses, if there are two or more of the spouses with either a marriage event or child birth event.
Developed using SQLiteSpy and should require no special extensions so it should run with any recent SQLite manager.
SpouseSort2.sql
2016-01-12 Superseded SpouseSort.sql to factor in birth/christen date of first-born children of unwed couples in the absence of a marriage event.
As always, test it on a copy of your database or make a backup first.
RootsMagic 4-7 (current) list the user-added roles in the Edit Fact Type dialog in the order that they were created, after the builtin roles such as Principal and Witness. For fact types to which many roles have been added, it is desirable that they be sorted alphabetically. While this should easily be done within the program for display purposes and has been requested repeatedly over years, until such an enhancement is provided here is a script that uses a brute force method to rearrange the rows in the data table so that the role names are presented alphabetically.
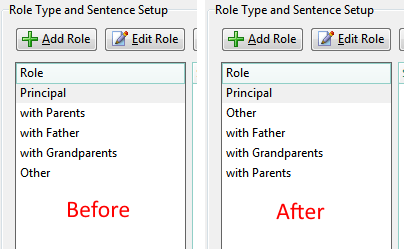
As far as I can tell, the script is harmless. There is no need to use RootsMagic’s Rebuild Indexes after its execution but it would be advisable to test it on a copy of your database or make a backup before applying it. It was developed using SQLiteSpy but uses no esoteric functions so it should run with any SQLite manager that supports a fake RMNOCASE collation extension..
Caveat: If a future version of RM increases the number of builtin roles to more than 58, every instance of 58 in the script must be revised accordingly else those builtin roles above the RoleID of 58 will be mixed up with a user-added role after a drag’n’drop or GEDCOM transfer to another RootsMagic database..
Tip: If you want the role names to appear in an order sorted by your preference, rename them prefixed by a number, e.g.:
If you have more than 9 roles, then use double digits:
01 with Parents
02 with Father
…
2023-02-19 Version for #RM8 added.
Duplication is declared if a pair of events:
Duplication is resolved in RM by:
To refresh the named group’s membership list to reflect corrections you may have made to resolve duplication of events, rerun the query to regenerate the RootsMagic group table and then, in RootsMagic, select a different group and then re-select the “SQL: Duplicate Events” group. You should see that names have disappeared from the group, provided you have corrected all the duplicate events for each person you worked on. The Quick Groups feature in RM7 and the Groups list in RM8 allow you to unmark a member from the group right from the Edit Person screen making it unnecessary to rerun the script unless you missed doing so.
To vary the parameter controlling how sensitive the query is to date differences, change this line at the end of the script:
WHERE ABS(SUBSTR(Date1,4,4) - SUBSTR(Date2,4,4)) <2 -- this controls how tight the year match must be. -- in future, the date comparison could call on a date calculator that could compute the difference in days ) ; --END of SCRIPT
A setting of “<2” permits two consecutive years which allows Dec 31, 1900 and Jan 1, 1901 to be considered duplicates as it does for Jan 1, 1900 and Dec 31, 1901. A setting “<1” requires the events to be in the same year.
Group-PersonsWithDuplicateEvents.sql rev 2018-07-07 bug fixed when no other existing group
RM8 Version 2023-02-19
RootsMagic has three different storage mechanisms for Nicknames:
Different outputs from RootsMagic have differing usage of these. Box charts cannot use Alternate Names and only include the primary name Nickname field if Prefix and Suffix are also included. Sentence templates for facts other than the Alternate Name type cannot access Alternate Names, cannot parse the nickname embedded in the primary Given field but can use the primary Nickname field. So there are outputs where it may be desirable that nicknames be embedded with the given name and others where it should not be. And as a database is built over time from a variety of sources, there may be inconsistency in the way nicknames are stored within the database.
This page offers a set of scripts that can manipulate where the nickname values are stored, globally and quickly, to optimise for a desired output and to make consistent.
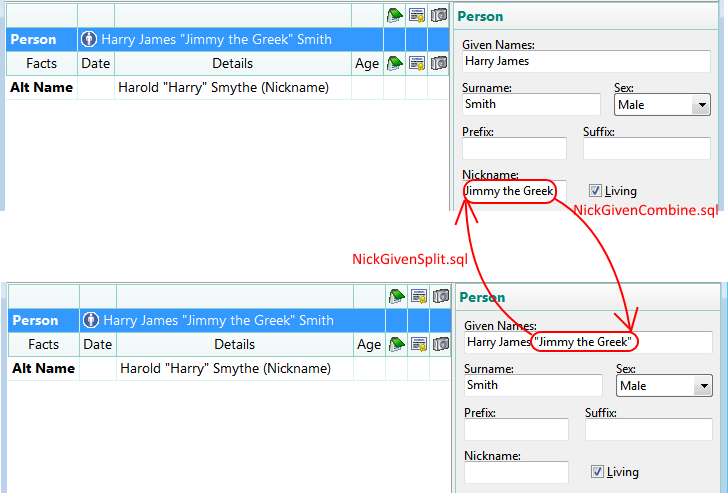
These two scripts can swap the nickname between the NickName field and the Given Names field. The splitter works only with quotation marks delimiting the nickname in the Givens field; the combiner puts the nickname in quotes in the Givens field. You can use RootsMagic Search and Replace function on the Given names to convert all instances of parentheses to double quotation marks.
NickGivenSplit.sql
NickGivenCombine.sql
This script returns Record Number and Names of Persons who have both an embedded Nickname and a value in the Nickname field. These cannot be processed by NickGivenCombine.sql and NickGivenSplit.sql and should be resolved in the database with one or the other but not both.
Includes those having parentheses to denote nickname in the Given field instead of quotes; parentheses not supported by other scripts in this series.
This script returns the Record Number and Nicknames of Persons who have both an Alternate Nickname and a Primary name with an embedded nickname or non-empty NickName field and the nickname values in the corresponding fields do not match. Use RIN to find the person in RootsMagic Explorer to revise as needed.
NickAltNameConflict.sql
UNDER CONSTRUCTION
-possibly converters between the nickname fields of Primary Name and Alternate Name of type Nickname but this would be complex.
As of RootsMagic 8 Preview 7.9.180, the traceability of where an image is used has changed little from what was described below for RM4. The need for an outboard query such as this is as high in early 2021 as it was in 2010. With some changes in tables from RM7, the Media-UsersList4.sql query does not run on RM8. Pat Jones revised it and applied a technique she describes at Common Table Expressions – The Building Blocks of SQL to streamline it:
For a version that works with databases from RM5 to RM7:
Media-UsersList4-RM7.sql
RootsMagic 4 falls short in handling media in several ways. One serious one is its inability to report fully all the ‘owners’ of the media, i.e., its terminology to describe what person, couple, event, source, citation, place or place detail to which a media item is attached, in sufficient detail that the attachment can be found. Trace-ability is essential to be able to make changes to an attachment’s properties, i.e., its caption, description, reference number, date, sort date, primary and scrapbook inclusion flags. RM4’s Report > Lists > Multimedia List does not even report usage by Sources or Source Details and fails to report the Place to which a Place Detail, having media attached, belongs. Similarly, the Media Gallery > Tools > “Show where this media is used” results are incomplete for media attached to Source Details or to Place Details, giving little or no clue to how you would navigate to the citation or Place where you could then drill down to the Media and edit the caption or other properties.
Here’s an example of what I mean:
Owner according to Media Gallery > Tools > “Show where this media is used”
Cens: 1891 Can: Ancestry.ca - FF2 (ff incomplete) (citation)
How can one possibly find the citation without at least the RIN or name of the person?
Users according to Media-UsersList query
(citation) WICKENS, Martha Jane "Jenny"-208 : RESIDENCE (FAMILY) ca 1891 : HOLDEN, Matthew Edwin-149 citing Cens: 1891 Can: Ancestry.ca - FF2 (ff incomplete) (citation) HOLDEN, Matthew Edwin-149 : RESIDENCE (FAMILY) ca 1891 : WICKENS, Martha Jane "Jenny"-208 citing Cens: 1891 Can: Ancestry.ca - FF2 (ff incomplete)
Both RM4 and the query show that the media file is attached to a citation but the new query provides explicit guidance to the citation via not only the name and RIN of the person but also the fact name and date so that the citing fact can be quickly found and its Citation Manager opened. The source name is shown (that’s all the Media Gallery shows apart from the caption and full filename) so it can be readily selected from the Citation Manager and the Source Detail Media Album opened therefrom and the media item selected by file name for the editing of its properties. That is the only way RM4 lets you get to the item’s properties; obviously, a road map is necessary. This query shows the route.
Media-UsersList.sql – original query, easier to modify, fast on smaller databases, bogs down on large ones
Media-UsersList3.sql ![]() – fast even on very large databases, larger sql file, harder to modify at the base SELECTs.
– fast even on very large databases, larger sql file, harder to modify at the base SELECTs.
Media-UsersList4.sql – as ver 3 but revised for RM5 and 6; prior versions work with RM4.
Using SQLite Expert Personal, make sure the following setting is checked for the thumbnail image to be shown:
 |
| Screenshot from SQLiteSpy which has no image display capability but does remember column widths within the same session and supports sorting on column regardless of an ORDER BY in the query. |
With the flurry of users of Family Tree Maker looking to migrate their database to RootsMagic, an outcry has gained volume because of the disappearance of some citations. This problem was described here in 2012 in Citations Invisible Revealed which offered two scripts, both of which are available in the RMtrix utility, one to find such citations for the Primary (Preferred Name), the other to convert them to citations for the Person. That was an irreversible conversion. In the hope that RootsMagic will eventually support citations for the Primary (Preferred) Name, this pair of scripts provides both conversion and reversion. As of 2015-12-24, RootsMagic is expected to issue an update that will do a similar conversion and an upgrade that will support citations for the Primary (Preferred) Name and revert these conversions. However, it will use a different value in the flag to make the citations reversible than was used in the initial scripts, necessitating these revised versions to be compatible.
Citations, Invisible – Convert to Personals + Flagged.sql rev 2015-12-24 Flags field now set bitwise on 1st bit instead of to 7
Citations, Invisible Revealed – Revert – Bitwise.sql 2015-12-24 Unsets 1st bit of Flags field instead of setting to 0
Caveat! To make it reversible, the converter uses the apparently unused Flags column in the CitationTable. The initial converter dated 2015-12-19 set this value to 7, corresponding to the original OwnerType value for the Citation Table record; the value that RootsMagic will use for this purpose will be the 1st bit set to 1, allowing the Flags field to be used for many bitwise flags. I cannot predict what the consequences might be for those records having a flag value of 7 set by the initial converter. If you used the now-deprecated, initial version of Citations, Invisible – Convert to Personals + Flagged.sql, it would be advisable to run this complementary script to revert them to the primary Name fact: Citations, Invisible Revealed – Revert.sql Then follow up with the revised converter above or wait for the RootsMagic update to do the same thing.
James Clouse posted this video to the RootsMagic Users Facebook Group showing how to use SQLiteSpy to open your database and run the conversion script. Click on the settings and select HD to avoid fuzziness.